|
|
|
|
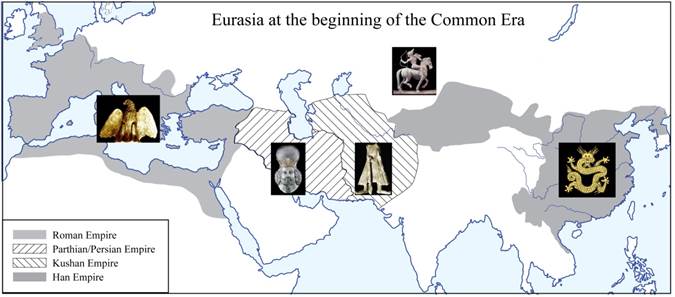
The beginning of
the Common Era was an age of empires. Four great empires – the Roman,
Parthian/Persian, Kushan, and Han – spanned mid-latitude Eurasia and northern
Africa. To their north, the nomadic empire of the Xiongnu was disintegrating
under Han pressure, but that of the Huns had not yet arrived. |
|||||||||||
|
The age of empires |
|||||||||||
|
Ancient
peoples at either end of Eurasia had notions of “the world,” the Chinese tianxia, Roman orbis terrarum, and Greek oikumenē. The Chinese and Roman Empires each
imagined itself covering the whole world. The Romans claimed imperium
orbis terrae,
domination over the earth, which they expressed by
placing the globe under the foot or on the palm of the statues of Goddess
Roma or emperors. The Chinese claimed yitong
tianxia 一統天下, unity under heaven. As soon
as Qin united China, it standardized laws, local government institutions,
coinage, weight, measure, even the gauge of carriages, so that vehicles ran
in the same ruts all across the empire. |
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|||
|
|
|||
|
The Mediterranean |
BCE |
中國 China |
|
|
Destruction of the citadel of |
c. 1150 |
|
|
|
|
c. 1066 – 771 |
西周 West Zhou dynasty |
|
|
Phoenician and Greek colonization |
c. 775 – c. 650 |
|
|
|
|
771 – 256 |
東周 East Zhou dynasty |
|
|
|
771 |
秦立國 State of Qin invested |
|
|
Traditional date of the foundation of |
753 |
|
|
|
|
722 - 481 |
春秋 Spring and Autumn period |
|
|
King Servius Tullius of |
c 579 – 543 |
|
|
|
|
c. 566 – 486 |
釋迦 Siddhartha (Buddha, in India) |
|
|
|
551 - 479 |
孔丘
Confucius |
|
|
Foundation of the |
509 |
|
|
|
Wars between |
490 - 449 |
|
|
|
Socrates |
470 - 399 |
|
|
|
|
453 - 221 |
戰國
Warring-state period |
|
|
Peloponnesian War between |
431 - 404 |
|
|
|
|
359 |
商鞅變法
Qin started political reform |
|
|
Latin League dissolved; |
338 |
|
|
|
Alexander the Great |
336 - 323 |
|
|
|
First Punic War between |
264 - 241 |
|
|
|
|
221 – 206 |
秦朝 Qin dynasty, beginning of imperial
China |
|
|
Second Punic War between |
218 - 202 |
|
|
|
|
206 -202 |
楚漢相爭
Civil war between Chu and Han |
|
|
|
202 – 1 CE |
西漢 Western Han dynasty |
|
|
|
200 |
單于立 Maodun became Chanyu of Xiongnu |
|
|
|
148 - 146 |
|
|
|
|
138 |
始營西域
China began westward expansion |
|
|
Roman civil wars |
49 - 27 |
|
|
|
Augustus as princeps |
27 – 14 CE |
|
|
|
|
c 2 |
佛學東漸
Buddhism entered China |
|
|
Jesus |
1 – 30 |
|
|
|
|
1 - 22 |
新朝 Xin Dynasty |
|
|
|
22 - 220 |
東漢 Eastern Han dynasty |
|
|
|
220 – 280 |
三國 Civil wars: three kingdoms |
|
|
Sassanians (Persians) overthrew |
226 |
|
|
|
Military anarchy in |
235 - 284 |
|
|
|
|
265 - 316 |
西晉 Western Jin dynasty |
|
|
|
316 |
洛陽淪陷 Fall of Luoyang |
|
|
|
316 - 589 |
東晉南北朝 China divided in North and South |
|
|
Foundation of |
324 |
|
|
|
Sack of |
410 |
|
|
|
End of the |
476 |
|
|
|
Mohammed |
571 - 632 |
|
|
|
|
589 - 618 |
隋朝 China reunited under Sui dynasty |
|
|
|
618 - 907 |
唐朝 Tang dynasty |
|
|
Muslim spread to |
633 - 655 |
|
|
|
Fall of |
1453 |
|
|
|
The |
CE |
China |
|